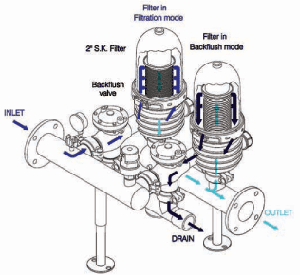
- Disc Filtration
- Automatic Disc (Spin Klin filtration technology)
- Automatic Self Cleaning Screen Filtration
- Media Filtration
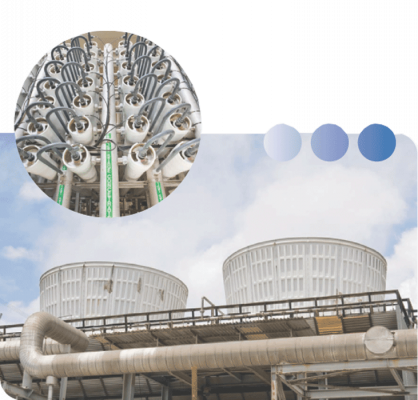
ARKAL’s dynamic solutions, including their patented automatic Spin Klin filtration technology incorporate extensive use of polymers for superb corrosion resistance against sea water, most chemicals and extremely harsh environments.
If this describes our application, Arkal Filtration Systems should be your first choice.
Leading Applications:
- Seawater filtration
- US/RO Membrane Protection
- Pre filtration for UV Plants
- Cooling Towers
- Marine and Offshore
- Petrochemical
- Aquaculture
Disc filtration:
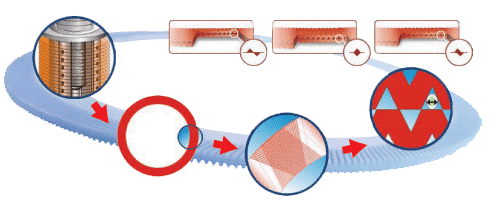

ARKAL Water Filtration Systems operate using a specially designed disc filtration technology. Thin, color-coded polypropylene or nylon discs are diagonally grooved on both sides to a specific micron size. A series of these discs are then stacked and compressed and a specially design spin. When stacked, the groove on top runs opposite to the groove below, creating a filtration element with a statistically significant series of valleys and traps for solids. The stack is enclosed in a corrosion and pressure resistant housing.
Disc filters are used before membranes and other equipment for superior protection, efficiency and corrosion resistance. They can also be used as standalone filtration systems for sea water cooling, aquaculture, cooling towers, marine systems etc.
Arkal disc filtration systems a available in manual or as automatic “Spine Klin” systems.
Table of filtration grades of disc filters:
| Color Code: | Blue | Yellow | Red | Black | Brown | Green | Purple | Gray |
| Mesh | 40 | 80 | 120 | 140 | – | – | – | – |
| Micron | 400 | 200 | 130 | 100 | 70 | 55 | 40 | 20 |
Advantages:

- Engineered for efficient operation with minimal maintenance.
- Flat, grooved plastic rings stack together to form the filter element.
- Depth filtration increasing filtration efficiency
- Greater holding capacity as water is filtered through the entire ring depth, not just the surface.
- During filtration, pressure increases and compresses the rings increasing efficiency and protecting the system from clogging.
- Degree of filtration is easily changed by replacing the disc rings with the desired mesh/micron size.
- Available in a range of sizes , degrees of filtration and flow capacities.
Automatic Spin Klin® disc filtration
Automatic Spin Klin Filter Batteries are fully automatic disc filters with polypropylene manifolds resistant to rust and corrosion from chemicals and weather. These filters utilize proven depth filtration technology optimizing your process, providing superior equipment protection and saving backflush water. Available in several configurations with flow ranges from 5 to 20,000m3/hr or more. the systems are quickly installed as filters are factory assembled and tested. Minimal maintenance is required due to very efficient backflushing.
Advantages: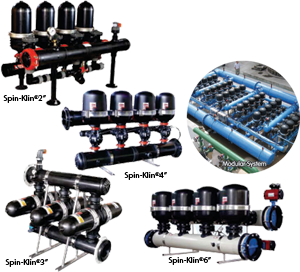

- Installation is quick as filters are factory assembled and tested.
- Manual cleaning is practically eliminated.
- Filtration grade versatility with filtration discs able to be changed quickly nd easily from 40 mesh up to 600 mesh (400-20 Micro)
- Less backflush time, optimizing the process and saving water.
- Each Spin Klin battery is capable of handling a wide operational flow range.
- Manufactured from engineered synthetics to prevent rust and corrosion meaning longer life and greater return an investment.
|


Automatic Self-cleaning Screen Filter
ARKAL’s Screen filter range utilize proven screen filtration technology to effective screen solides whilst optimizing and saving water. Available in several configurations with flow ranges from 5 to 2,000 m3/hr and more.

Quick installation as filters are factory assembled and tested. Minimal maintenance is required due to reliable backflushing.
They are perfect for situations where Spin Klin cannot be used i.e. filtration grade too large, high pressure and/or temperature.
The Technology


retention point for solids. As dirty water passes through the vessel from the inside to the outside of the screen, the larger particles are physically prevented from passing and are retained on the screen.
Screen Sizes are available from 3,000 to 20 micron
The effective filtration area of a screen filter can be quite high and the initial “clean” head loss is quite low. The differential pressure however, can build up quickly, making and effective cleaning schedule essential. Screen filters can be cleaned manually or automatically, like all other types of filter.

Manual cleaning usually involves removing the filter element and hasting/brushing it clean. Automatic cleaning is activated automatically as the particles, trapped on the inside surface of the fine screen create a differential pressure build up. A number of cleaning methods are available.
Advantages:
- Installation is quick as filters are factory assembled and tested, arriving on site ready for connection and immediate operation.
- Less maintenance is required as the Dirt collector and Suction nozzle perform reliably during backflush Manual cleaning is practically eliminated.
- Filtration grade versatility from 20 – 3,000 Micron.
- Less backflush time means more uniform application of water in the field, optimizing the process and saving water.
- In-built coarse screen designed to protect the main line screen
Rotating Brush Cleaning
A brush rotates over the screen element dislodging the “filter cake” and a purge valve flushes the dirt out through a drain whilst the system is under pressure.


Vacuum Scanner Cleaning
A rotating vacuum scanner lifts “filter cake” off the screen without making physical contact. The rotation and linear movement of the scanner allow it to reach every part of the screen in minimal time. This system can be very effective and does not damage the screen as a brush may do.
AGF all plastic media filters
The Technology


Sand media filters operate by separating the suspended materials in unfiltered water as it flows through a bed of media in a pressurized tank. the recommend media, crushed basalt, quartz sand or catalytic media, have many varying aperture sizes (creating the micron rating) that cause the water to flow through a myriad of passages on it’s way from the inlet to the outlet of the filter.
Sand Media
Due to the large volume and contact area between the water and the media/gravel particles, various physical forces are put into effect and act to retain the contaminating particles.
the efficiency of large particle retention is high as long as the gravel is kept clean. The catalytic media type applies an additional chemical-physical attraction between the media and particles – especially those of organic nature, giving more efficient organic material separation. In addition, the round shaped particles degrade more quickly and their cleaning requires less water in comparison with other media types.
Filtration Process
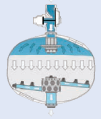

During the filtration process, unfiltered water enters the AGF media filter system via the inlet
manifold and the three stage distributor plate therefore reaching the media bed with minimal disturbance. Contaminants are entrapped as the water flows through the media bed. 55 mushrooms in the under drain create uniform collection of the filtered water whilst preventing the media from being washed way.
During filtration, head loss across the filter media will increase according to the accumulation of solids within the media. When it reaches the limit set by the hydraulic conditions of the system, the media will be cleaned of the accumulated solids by way of the back flush process.
Backwash Process


Periodic back flushing is necessary to cleanse the media bed of accumulated contaminants. During the back flushing process, the flow of clean, filtered water from one or more tanks in the battery is reversed through one filter at a time via a 3-way back flush valve.
As the flow is reversed, the media bed is floated via hydraulic turbulence, and contaminants are flushed out to back flush manifold, through the back flush port of the 3-way valve. The design of the under drain system is critical to ensure uniform flotation of the media bed during the back flush process, and is critical for minimizing the amount of back flush water required to rapidly expel the contaminants from the media bed. Once the back flush is completed, the valves return to filtration mode and the next filter will back flush in turn.